Solved Paper III
CBSE UGC NET Computer Science November 2017
Read more: http://www.netcomputerscience.com
1.
In 8085 microprocessor which of the following
flag(s) is (are) affected by an arithmetic operation?
(1) AC flag
Only
(2) CY flag
Only
(3) Z flag
Only
(4) AC, CY,
Z flags
Answer: 4
Explaination:-
- Auxiliary Carry (AC): In an arithmetic operation, when a carry is generated by digit D3 and passed to digit D4, the AC flag is set.
- Carry flag (CY): After an addition of two numbers, if the sum in the accumulator is larger than eight bits, then the flip-flop uses to indicate a carry called the Carry flag – which is set to one.
- Zero Flag (Z): When an arithmetic operation results in zero , the flip-flop called the Zero flag - which is set to one.
- Sign (S): It is set to 1, if bit D7 of the result = 1; otherwise reset. D7 is the first digit of a binary number.
- Parity (P): If the result has an even number of 1s, the flag is set to 1; for an odd number of 1s the flag is reset.
2. In
8085 microprocessor the address bus is of .................... bits.
(1) 4
(2) 8
(3) 16
(4) 32
Answer: 3
Explaination:-
Address Bus is unidirectional.In Intel 8085 microprocessor, Address bus was of 16
bits. This means that Microprocessor 8085 can transfer maximum 16 bit
address which means it can address 65,536 different memory locations.
3. In
the architecture of 8085 microprocessor match the following:
List - I
(a)
Processing unit
(b)
Instruction unit
(c) Storage
and Interface unit
List - II
(i)
Interrupt
(ii) General
purpose Register
(iii) ALU
(iv) Timing
and Control
Code :
(a) (b) (c)
(1) (iv) (i)
(ii)
(2) (iii)
(iv) (ii)
(3) (ii) (iii) (i)
(4) (i) (ii) (iv)
Answer: 2
4. Which
of the following addressing mode is best suited to access elements of an array
of contiguous memory locations?
(1) Indexed
addressing mode
(2) Base
Register addressing mode
(3) Relative
address mode
(4)
Displacement mode
Answer: 1
Explanation: Indexed addressing mode is best suited for accessing an array in contiguous memory location.
Indexed addressing mode: The operand’s offset is the sum of the content of an index register SI or DI and an 8 bit or 16 bit displacement.
Example:MOV AX, [SI +05]
5. Which
of the following is correct statement?
(1) In
memory - mapped I/O, the CPU can manipulate I/O data residing in interface registers
that are not used to manipulate memory words.
(2) The
isolated I/O method isolates memory and I/O addresses so that memory address range
is not affected by interface address assignment.
(3) In
asynchronous serial transfer of data the two units share a common clock.
(4) In
synchronous serial transmission of data the two units have different clocks.
Answer: 2
Explaination
(3) In asynchronous serial transfer of data the two units have a different clock.
Explaination
(3) In asynchronous serial transfer of data the two units have a different clock.
(4) In
synchronous serial transmission of data the two units have same clocks.
6. A
micro-instruction format has micro-ops field which is divided into three
subfields F1, F2, F3 each having seven distinct micro-operations, condition
field CD for four status bits, branch field BR having four options used in
conjunction with address field ADF. The address space is of 128 memory
locations. The size of micro-instruction is:
(1) 17 bits
(2) 20 bits
(3) 24 bits
(4) 32 bits
Answer: 2
7. Consider
the following four schedules due to three transactions (indicated by the
subscript) using read and write on a data item X, denoted by r(X) and w(X)
respectively. Which one of them is conflict serializable?
S1
: r1(X); r2(X); w1(X); r3(X); w2(X)
S2
: r2(X); r1(X); w2(X); r3(X); w1(X)
S3
: r3(X); r2(X); r1(X); w2(X); w1(X)
S4
: r2(X); w2(X); r3(X); r1(X); w1(X)
(1) S1
(2) S2
(3) S3
(4) S4
Answer: 4
8. Suppose
a database schedule S involves transactions T1, T2,
.............,Tn. Consider the precedence graph of S with vertices
representing the transactions and edges representing the conflicts. If S is
serializable, which one of the following orderings of the vertices of the precedence
graph is guaranteed to yield a serial schedule?
(1)
Topological order
(2) Depth -
first order
(3) Breadth
- first order
(4)
Ascending order of transaction indices
Answer: 1
9. If
every non-key attribute is functionally dependent on the primary key, then the
relation is in ....................
(1) First
normal form
(2) Second
normal form
(3) Third
normal form
(4) Fourth
normal form
Answer: 3
10. Consider
a relation R (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H), where each attribute is atomic, and
following functional dependencies exist.
CH → G
A → BC
B → CFH
E → A
F → EG
The relation
R is ....................
(1) in 1NF
but not in 2NF
(2) in 2NF
but not in 3NF
(3) in 3NF
but not in BCNF
(4) in BCNF
Answer: 1
11.
Given two relations R1(A, B) and R2(C,
D), the result of following query
Select
distinct A, B from R1, R2
is
guaranteed to be same as R1 provided one of the following condition
is satisfied.
(1) R1
has no duplicates and R2 is empty.
(2) R1
has no duplicates and R2 is non - empty.
(3) Both R1
and R2 have no duplicates.
(4) R2
has no duplicates and R1 is non - empty.
Answer: 2
12. Consider
a schema R(A, B, C, D) and following functional dependencies.
A → B
B → C
C → D
D → B
Then
decomposition of R into R1(A, B), R2(B, C) and R3(B,
D) is ..................
(1)
Dependency preserving and lossless join.
(2) Lossless
join but not dependency preserving.
(3)
Dependency preserving but not lossless join.
(4) Not
dependency preserving and not lossless join.
Answer: 1
13. Which
of the following is not a component of Memory tube display?
(1) Flooding
gun
(2)
Collector
(3) Ground
(4) Liquid
Crystal
Answer: 4
14. Which
of the following is not true in case of Oblique Projections?
(1) Parallel
projection rays are not perpendicular to the viewing plane.
(2) Parallel
lines in space appear parallel on the final projected image.
(3) Used
exclusively for pictorial purposes rather than formal working drawings.
(4)
Projectors are always perpendicular to the plane of projection.
Answer: 4
15. With
respect to CRT, the horizontal retrace is defined as :
(1) The path
an electron beam takes when returning to the left side of the CRT.
(2) The path
an electron beam takes when returning to the right side of the CRT.
(3) The
technique of turning the electron beam off while retracing.
(4) The
technique of turning the electron beam on/off while retracing.
Answer: 1
16. Find
the equation of the circle x2+y2=1 in terms of x'y'
coordinates, assuming that the xy coordinate system results from a scaling of 3
units in the x' direction and 4 units in the y' direction.
(1) 3(x')2
+ 4(y')2 = 1
(2) (x'/3)2
+ (y'/4)2 = 1
(3) (3x')2
+ (4y')2 = 1
(4) 1/3(x')2
+ 1/4(y')2 = 1
Answer: 2
17. Find
the normalization transformation that maps a window whose lower left corner is
at (1, 1) and upper right corner is at (3, 5) onto a viewport that is the
entire normalized device screen.
Answer: 1
18. The
three aspects of Quantization, programmers generally concerned with are:
(1) Coding
error, Sampling rate and Amplification
(2) Sampling
rate, Coding error and Conditioning
(3) Sampling
rate, Aperture time and Coding error
(4) Aperture
time, Coding error and Strobing
Answer: 3
19. The
logic of pumping lemma is an example of ....................
(1)
iteration
(2)
recursion
(3) the
divide and conquer principle
(4) the
pigeon - hole principle
Answer: 4
20. Heap
allocation is required for languages that :
(1) use
dynamic scope rules
(2) support
dynamic data structures
(3) support
recursion
(4) support
recursion and dynamic data structures
Answer: 2
21.
Pumping lemma for regular language is
generally used for proving:
(1) whether
two given regular expressions are equivalent
(2) a given
grammar is ambiguous
(3) a given
grammar is regular
(4) a given
grammar is not regular
Answer: 4
22. Which
of the following problems is undecidable?
(1) To
determine if two finite automata are equivalent
(2)
Membership problem for context free grammar
(3)
Finiteness problem for finite automata
(4)
Ambiguity problem for context free grammar
Answer: 4
23. Finite
state machine can recognize language generated by ....................
(1) Only
context free grammar
(2) Only
context sensitive grammar
(3) Only
regular grammar
(4) any
unambiguous grammar
Answer: 3
24. The
language L = {ai b ci | i ≥ 0} over the alphabet {a, b,
c} is:
(1) a
regular language.
(2) not a
deterministic context free language but a context free language.
(3)
recursive and is a deterministic context free language.
(4) not
recursive.
Answer: 3
25. Suppose
we want to download text documents at the rate of 100 pages per second. Assume that
a page consists of an average of 24 lines with 80 characters in each line. What
is the required bit rate of the channel?
(1) 192 kbps
(2) 512 kbps
(3) 1.248
Mbps
(4) 1.536
Mbps
Answer: 4
26. Quadrature
Amplitude Modulation means changing both:
(1)
Frequency and phase of the carrier.
(2)
Frequency and Amplitude of the carrier.
(3)
Amplitude and phase of the carrier.
(4)
Amplitude and Wavelength of the carrier.
Answer: 3
27. If
a file consisting of 50,000 characters takes 40 seconds to send, then the data
rate is ........................
(1) 1 kbps
(2) 1.25
kbps
(3) 2 kbps
(4) 10 kbps
Answer: 4
28. Match
the following:
List - I
(a) Data
link layer
(b) Network
layer
(c)
Transport layer
(d)
Presentation layer
List - II
(i)
Encryption
(ii)
Connection control
(iii)
Routing
(iv) Framing
Code :
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(1) (iv)
(iii) (i) (ii)
(2) (iii) (iv)
(ii) (i)
(3) (iv)
(ii) (iii) (i)
(4) (iv)
(iii) (ii) (i)
Answer: 4
29. The
address of a class B host is to be split into subnets with a 6 - bit subnet
number. What is the maximum number of subnets and maximum number of hosts in
each subnet?
(1) 62
subnets and 1022 hosts
(2) 64
subnets and 1024 hosts
(3) 62
subnets and 254 hosts
(4) 64
subnets and 256 hosts
Answer: 1
30. Which
of the following statements are true?
(a) The
fragmentation fields in the base header section of IPv4 have moved to the fragmentation
extension header in IPv6.
(b) The
authentication extension header is new in IPv6.
(c) The
record route option is not implemented in IPv6.
Code :
(1) (a) and
(b) Only
(2) (b) and
(c) Only
(3) (a) and
(c) Only
(4) (a), (b)
and (c)
Answer: 4
31.
Consider a full binary tree with n internal
nodes, internal path length i, and external path length e. The internal path
length of a full binary tree is the sum, taken over all nodes of the tree, of
the depth of each node. Similarly, the external path length is the sum, taken
over all leaves of the tree, of the depth of each leaf.
Which of the
following is correct for the full binary tree?
(1) e = i + n
(2) e = i + 2n
(3) e = 2i +
n
(4) e = 2n
+ i
Answer: 2
32. You
are given a sequence of n elements to sort. The input sequence consists of n/k subsequences,
each containing k elements. The elements in a given subsequence are all smaller
than the elements in the succeeding subsequence and larger than the elements in
the preceding subsequence. Thus, all that is needed to sort the whole sequence
of length n is to sort the k elements in each of the n/k subsequences.
The lower
bound on the number of comparisons needed to solve this variant of the sorting
problem is:
(1) Ω(n)
(2) Ω(n/k)
(3) Ω(n lg
k)
(4) Ω(n/k lg
n/k)
Answer: 3
33. Consider
the recurrence relation:
T (n) =
8T(n/2) + Cn, if n > 1
= b, if n =1
Where b and
c are constants.
The order of
the algorithm corresponding to above recurrence relation is:
(1) n
(2) n2
(3) n lg n
(4) n3
Answer: 4
34. Consider
the following two sequences :
X = <B,
C, D, C, A, B, C>
and Y =
<C, A, D, B, C, B>
The length
of longest common subsequence of X and Y is:
(1) 5
(2) 3
(3) 4
(4) 2
Answer: 3
35. A
text is made up of the characters a, b, c, d, e each occurring with the
probability 0.11, 0.40, 0.16, 0.09 and 0.24 respectively. The optimal Huffman
coding technique will have the average length of:
(1) 2.40
(2) 2.16
(3) 2.26
(4) 2.15
Answer: 2
36. An
undirected graph G (V, E) contains n (n > 2) nodes named v1, v2,...,vn.
Two nodes vi and vj are connected if and only if 0 < |
i – j | ≤ 2. Each edge (vi, vj) is assigned a weight i+j.
The cost of
the minimum spanning tree of such a graph with 10 nodes is :
(1) 88
(2) 91
(3) 49
(4) 21
Answer: 2
37. An
XML document that adheres to syntax rules specified by XML 1.0 specification in
that it must satisfy both physical and logical structured, is called :
(1) Well -
formed
(2)
Reasonable
(3) Valid
(4)
Sophisticated
Answer: 1
38. Which
of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding Java Servelets?
(a) A Java
Servelet is a server-side component that runs on the web server and extends the
capabilities of a server.
(b) A
Servelet can use the user interface classes like AWT or Swing.
Code :
(1) Only (a)
is TRUE.
(2) Only (b)
is TRUE.
(3) Both (a)
and (b) are TRUE.
(4) Neither
(a) nor (b) is TRUE.
Answer: 1
39. Consider
the following HTML table definition :
<table
border=1>
<tr>
<td
colspan=2> Text A </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Text B </td>
<td>
Text C </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td
rowspan=2> Text D </td>
<td>
Text E </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Text F </td>
</tr>
</table>
The above
HTML code would render on screen as :
Answer: 3
40. Which
of the following statements is/are TRUE?
(a) In HTML,
character entities are used to incorporate external content into a web page, such
as images.
(b) Once a
web server returns a cookie to a browser, the cookie will be included in all future
requests from the browser to the same server.
Code :
(1) Only (a)
is TRUE.
(2) Only (b)
is TRUE.
(3) Both (a)
and (b) are TRUE.
(4) Neither
(a) nor (b) is TRUE.
Answer: 4
41.
Which of the following statements is/are TRUE
regarding JAVA?
(a)
Constants that cannot be changed are declared using the ‘static’ keyword.
(b) A class
can only inherit one class but can implement multiple interfaces.
Code :
(1) Only (a)
is TRUE.
(2) Only (b)
is TRUE.
(3) Both (a)
and (b) are TRUE.
(4) Neither
(a) nor (b) is TRUE.
Answer: 2
42. What
is the output of the following JAVA program?
Class Test
{
public
static void main (String [ ] args)
{
Test
obj = new Test ( );
obj.start
( );
}
void
start ( )
{
String
stra=”do”;
String
strb = method (stra);
System.out.print(“:”
+ stra + strb);
}
String
method (String stra)
{
stra=stra+”good”;
System.out.print
(stra);
return
“good”;
}
}
(1) dogood :
dogoodgood
(2) dogood :
gooddogood
(3) dogood :
dodogood
(4) dogood :
dogood
Answer: 4
43. Statistical
software quality assurance in software engineering involves ................
(1) using
sampling in place of exhaustive testing of software.
(2)
surveying customers to find out their opinions about product quality.
(3) tracing
each defect to its underlying cause, isolating the vital few causes, and moving
to correct them.
(4) tracing
each defect to its underlying causes, and using the Pareto principle to correct
each problem found.
Answer: 3
44. Which
of the following statements is/are FALSE with respect to software testing?
S1 :
White-box tests are based on specifications; better at telling whether program
meets specification, better at finding errors of ommission.
S2 :
Black-box tests are based on code; better for finding crashes, out of bounds
errors, file not closed errors.
S3 : Alpha
testing is conducted at the developer’s site by a team of highly skilled
testers for software that is developed as a product to be used by many
customers.
(1) Only S1
and S2 are FALSE.
(2) Only S1
and S3 are FALSE.
(3) Only S2
and S3 are FALSE.
(4) All of
S1, S2, and S3 are FALSE.
Answer: 1
45. A
signal processor software is expected to operate for 91.25 days after repair,
and the mean software repair time is expected to be 5 minutes. Then, the
availability of the software is :
(1) 96.9862%
(2) 97.9862%
(3) 98.9962%
(4) 99.9962%
Answer: 4
46. Consider
the method mcq ( ) :
int mcq
(boolean a, boolean b, boolean c, boolean d)
{
int
ans=1;
if
(a) {ans = 2;}
else
if (b) {ans = 3;}
else
if (c) {
if
(d) {ans=4;}
}
return
ans ;
}
If
M1 = Number
of tests to exhaustively test mcq ( );
M2 = Minimum
number of tests to achieve full statement coverage for mcq ( ); and
M3 = Minimum
number of tests to achieve full branch coverage for mcq ( );
then (M1,
M2, M3) = ....................
(1) (16, 3,
5)
(2) (8, 5,
3)
(3) (8, 3,
5)
(4) (16, 4,
4)
Answer: 1
47. A
simple stand - alone software utility is to be developed in ’C’ programming by
a team of software experts for a computer running Linux and the overall size of
this software is estimated to be 20,000 lines of code. Considering (a, b) =
(2.4, 1.05) as multiplicative and exponention factor for the basic COCOMO
effort estimation equation and (c, d)=(2.5, 0.38) as multiplicative and
exponention factor for the basic COCOMO development time estimation equation,
approximately how long does the software project take to complete?
(1) 10.52
months
(2) 11.52
months
(3) 12.52
months
(4) 14.52
months
Answer: 2
48. In
Software Configuration Management (SCM), which of the following is a use-case
supported by standard version control systems?
(a) Managing
several versions or releases of a software
(b) Filing
bug reports and tracking their progress
(c) Allowing
team members to work in parallel
(d)
Identifying when and where a regression occurred
Code :
(1) Only
(a), (c), and (d)
(2) Only
(a), (b), and (c)
(3) Only
(a), (b), and (d)
(4) Only
(b), (c), and (d)
Answer: 1
49. Consider
the following four processes with the arrival time and length of CPU burst
given in
milliseconds
:
Process
Arrival Time Burst Time
P1 0
8
P2 1
4
P3 2
9
P4 3
5
The average
waiting time for preemptive SJF scheduling algorithm is .................
(1) 6.5 ms
(2) 7.5 ms
(3) 6.75 ms
(4) 7.75 ms
Answer: 1
50. Consider
a virtual page reference string 7, 0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 4, 2, 3, 0, 3, 2, 1, 2, 0,
1, 7, 0, 1. Suppose a demand paged virtual memory system running on a computer
system such that the main memory has 3 page frames. Then ................. page
replacement algorithm has minimum number of page faults.
(1) FIFO
(2) LIFO
(3) LRU
(4) Optimal
Answer: 4
51.
User level threads are threads that are
visible to the programmer and are unknown to the kernel. The operating system
kernel supports and manages kernel level threads. Three different types of
models relate user and kernel level threads.
Which of the
following statements is/are true?
(a) (i) The
Many - to - one model maps many user threads to one kernel thread
(ii) The one - to - one model maps one
user thread to one kernel thread
(iii) The many - to - many model maps many
user threads to smaller or equal kernel
threads
(b) (i) Many - to - one model maps many kernel
threads to one user thread
(ii) One - to - one model maps one kernel
thread to one user thread
(iii) Many - to - many model maps many
kernel threads to smaller or equal user
threads
Code :
(1) (a) is
true; (b) is false
(2) (a) is
false; (b) is true
(3) Both (a)
and (b) are true
(4) Both (a)
and (b) are false
Answer: 1
52. Consider
a system with five processes P0 through P4 and three resource types A, B and C.
Resource type A has seven instances, resource type B has two instances and
resource type C has six instances suppose at time T0 we have the following
allocation.
If we
implement Deadlock detection algorithm we claim that system is
..................
(1)
Semaphore
(2) Deadlock
state
(3) Circular
wait
(4) Not in
deadlock state
Answer: Marks to all
53. Consider
a disk queue with requests for I/O to blocks on cylinders 98, 183, 37, 122, 14,
124, 65, 67. Suppose SSTF disk scheduling algorithm implemented to meet the
requests then the total number of head movements are ................... if the
disk head is initially at 53.
(1) 224
(2) 248
(3) 236
(4) 240
Answer: 3
54. The
Bounded buffer problem is also known as ..................
(1) Producer
- consumer problem
(2) Reader -
writer problem
(3) Dining
Philosophers problem
(4) Both (2)
and (3)
Answer: 1
55. In
Artificial Intelligence (AI), which agent deals with happy and unhappy state?
(1) Simple
reflex agent
(2) Model
based agent
(3) Learning
agent
(4) Utility
based agent
Answer: 4
56. If
b is the branching factor and m is the maximum depth of the search tree, what
is the space complexity of greedy search?
(1) O(b+m)
(2) O(bm)
(3) O(bm)
(4) O(mb)
Answer: 3
57. Let
P, Q, R and S be Propositions. Assume that the equivalences P⇔(Q∨¬Q) and Q⇔R hold. Then the truth value of the formula
(P∧Q)⇒((P∧R)∨S) is always :
(1) True
(2) False
(3) Same as
truth table of Q
(4) Same as
truth table of S
Answer: 1
58. “If
X, then Y unless Z” is represented by which of the following formulae in
propositional
logic?
(1) (X ∧ Y) → ¬ Z
(2) (X ∧ ¬ Z) → Y
(3) X → (Y ∧ ¬ Z)
(4) Y → (X ∧ ¬ Z)
Answer: 2
59. Consider
the following two well-formed formulas in prepositional logic.
F1 : P ⇒ ¬ P
F2 : (P ⇒ ¬ P) ∨ (¬ P ⇒ P)
Which of the
following statements is correct?
(1) F1 is
Satisfiable, F2 is valid
(2) F1 is
unsatisfiable, F2 is Satisfiable
(3) F1 is
unsatisfiable, F2 is valid
(4) F1 and
F2 both are Satisfiable
Answer: 1
60. Standard
planning algorithms assume environment to be .................
(1) Both
deterministic and fully observable
(2) Neither
deterministic nor fully observable
(3)
Deterministic but not fully observable
(4) Not
deterministic but fully observable
Answer: 1
61.
Which of the following statements is not
correct?
(1) Every
recursive language is recursively enumerable.
(2) L = {0n
1n 0n | n=1, 2 , 3, ....} is recursively enumerable.
(3)
Recursive languages are closed under intersection.
(4)
Recursive languages are not closed under intersection.
Answer: 4
62. Context
free grammar is not closed under :
(1)
Concatenation
(2)
Complementation
(3) Kleene
Star
(4) Union
Answer: 2
63. Consider
the following languages :
L1
= {am bn | m ≠ n}
L2
= {am bn | m = 2n+1}
L3
= {am bn | m ≠ 2n}
Which one of
the following statement is correct?
(1) Only L1
and L2 are context free languages
(2) Only L1
and L3 are context free languages
(3) Only L2
and L3 are context free languages
(4) L1,
L2 and L3 are context free languages
Answer: 4
64. A
4×4 DFT matrix is given by :
(j2=−1)
Where values
of x and y are ..........., ............. respectively.
(1) 1, −1
(2) −1, 1
(3) −j, j
(4) j, −j
Answer: 4
65. Entropy
of a discrete random variable with possible values {x1, x2,
..., xn} and probability density function P(X) is :
The value of
b gives the units of entropy. The unit for b=10 is :
(1) bits
(2) bann
(3) nats
(4) deca
Answer: Marks to all
66. For
any binary (n, h) linear code with minimum distance (2t+1) or greater
(1) 2t+1
(2) t+1
(3) t−1
(4) t
Answer: 4
67. Which
of the following is a valid reason for causing degeneracy in a transportation problem?
Here m is no. of rows and n is no. of columns in transportation table.
(1) When the
number of allocations is m+n−1.
(2) When two
or more occupied cells become unoccupied simultaneously.
(3) When the
number of allocations is less than m+n−1.
(4) When a
loop cannot be drawn without using unoccupied cells, except the starting cell of
the loop.
Answer: 3
68. Consider
the following LPP :
Max Z=15x1+10x2
Subject to
the constraints
4x1+6x2
≤ 360
3x1+0x2
≤ 180
0x1+5x2
≤ 200
x1,
x2 ≥ 0
The solution
of the LPP using Graphical solution technique is :
(1) x1=60,
x2=0 and Z=900
(2) x1=60,
x2=20 and Z=1100
(3) x1=60,
x2=30 and Z=1200
(4) x1=50,
x2=40 and Z=1150
Answer: 2
69. Consider
the following LPP :
Min Z=2x1+x2+3x3
Subject to :
x1−2x2+x3
≥ 4
2x1+x2+x3
≤ 8
x1−x3
≥ 0
x1,
x2, x3 ≥ 0
The solution
of this LPP using Dual Simplex Method is :
(1) x1=0,
x2=0, x3=3 and Z=9
(2) x1=0,
x2=6, x3=0 and Z=6
(3) x1=4,
x2=0, x3=0 and Z=8
(4) x1=2,
x2=0, x3=2 and Z=10
Answer: 3
70. Consider
a Takagi - Sugeno - Kang (TSK) Model consisting of rules of the form :
If x1
is Ai1 and ... and xr is Air
THEN y =fi(x1,
x2, ..., xr) = bi0+bi1 x1+...+bir
xr
assume, αi
is the matching degree of rule i, then the total output of the model is given
by:
Answer: 2
71.
Consider a single perceptron with sign
activation function. The perceptron is represented by weight vector [0.4 −0.3
0.1]t and a bias θ=0. If the input vector to the perceptron is X=[0.2
0.6 0.5] then the output of the perceptron is :
(1) 1
(2) 0
(3) −0.05
(4) −1
Answer: 4
72. The
Sigmoid activation function f(t) is defined as :
Answer: 4
73. Consider
the following statements :
(a) UNIX
provides three types of permissions
*
Read
*
Write
*
Execute
(b) UNIX
provides three sets of permissions
*
permission for owner
*
permission for group
*
permission for others
Which of the
above statement/s is/are true?
(1) Only (a)
(2) Only (b)
(3) Both (a)
and (b)
(4) Neither
(a) nor (b)
Answer: 3
74. Which
of the following routing technique / techniques is / are used in distributed
systems?
(a) Fixed
Routing
(b) Virtual
Routing
(c) Dynamic
Routing
Code :
(1) (a) only
(2) (a) and
(b) only
(3) (c) only
(4) All (a),
(b), (c)
Answer: 4
75. Match
the following WINDOWS system calls and UNIX system calls with reference to
process control and File manipulation.
Windows
(a) Create -
process ()
(b)
WaitForSingleObject ()
(c)
CreateFile ()
(d)
CloseHandle ()
UNIX
(i) Open ()
(ii) Close ()
(iii) Fork ()
(iv) Wait ()
Code :
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(1) (iii)
(iv) (i) (ii)
(2) (iv)
(iii) (i) (ii)
(3) (iv)
(iii) (ii) (i)
(4) (iii)
(iv) (ii) (i)
Answer: 1






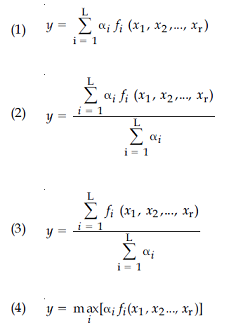

No comments:
Post a Comment